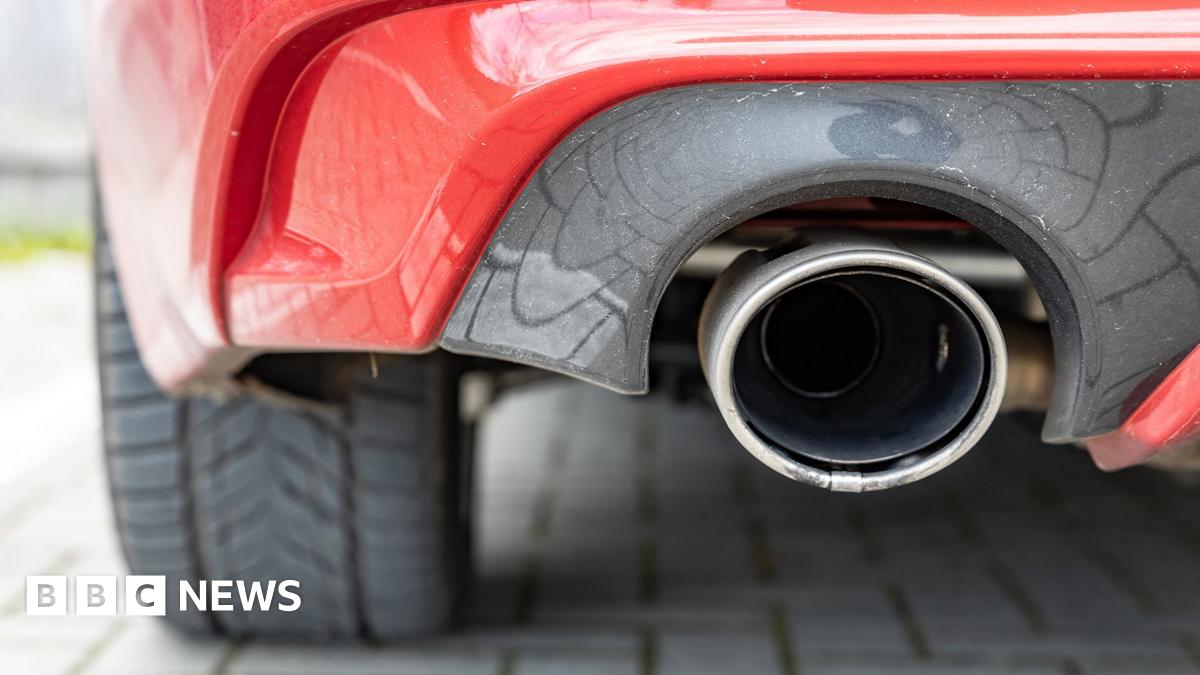
A major lawsuit against five leading carmakers accused of cheating on emissions tests has started at the High Court.
The trial is the latest chapter of what has become known as the "dieselgate" scandal, with the companies facing allegations they used software to allow their cars to reduce emissions of harmful gases under test conditions.
Lawyers say the case is the largest class action in English and Welsh legal history, and could eventually involve 1.6 million car owners.
The five carmakers – Mercedes, Ford, Peugeot/Citroën, Renault and Nissan – all deny the accusations.
These companies have been chosen by the court as lead defendants to be tried first as the case is so big. They have been accused by 220,000 car owners of misleading them over emissions tests.
But depending on the outcome of this case, nine other carmakers are facing similar claims.
The dieselgate scandal first emerged in September 2015, when the US Environmental Protection Agency accused Volkswagen of installing software – known as "defeat devices" – on diesel cars to lower readings of the cars' nitrogen oxide emissions.
In 2020, the High Court ruled that Volkswagen had used defeat devices in breach of European Union rules to pass emissions tests.
Volkswagen settled a class action out of court, paying £193m to 91,000 British motorists.
The company has so far paid out more than €32bn (£27.8bn) over the scandal, mostly in the US.
Lawyers representing drivers said that at the time of the scandal, "the unique selling point of diesel cars was their fuel/CO2 economy".
"Manufacturers wanted to sell vehicles with all the cost advantages of diesel but the performance (acceleration, associated drivability, lower engine noise) and convenience of petrol cars."
The lawyers will try to show car buyers were deceived about the environmental performance of their vehicles – and that some cars still on the road today are pumping out more toxic pollutants than they should.
The companies involved in the case insist that, unlike Volkswagen, they have never cheated.
They will argue in court that the software they used was legal and necessary to protect their engines from harm.
The High Court will decide whether systems installed in diesel cars by the five carmakers were designed to cheat clean air laws.
It is alleged the "defeat devices" allowed a car to identify when it was in a test scenario. It would then run its engine at below normal power and performance levels in order to record lower readings of nitrogen oxides.
Lawyers for the motorists will claim they were deceived about how environmentally friendly the vehicles were, and that the cars still on the road are continuing to emit dangerous levels of pollution.
A judgement is not expected until summer 2026. If the court finds against the carmakers, a further trial to determine levels of compensation is expected to begin in autumn 2026.
Martyn Day of Leigh Day, which is one of the 22 law firms representing drivers, said: "A decade after the Dieselgate scandal first came to light, 1.6 million UK motorists now get their chance to establish at trial whether their vehicles contained technology designed to cheat emissions tests."
He said that if the allegations against the car firms are upheld in court it "would demonstrate one of the most egregious breaches of corporate trust in modern times".
"It would also mean that people across the UK have been breathing in far more harmful emissions from these vehicles than they were told about, potentially putting the health of millions at risk."
The companies involved have said the claims against them are without merit.
A spokesperson for Mercedes said the mechanisms used in tests were "justifiable from a technical and legal standpoint".
Renault and Stellantis, which owns Peugeot and Citroen, said the vehicles it sold were compliant with regulations at the time.
Ford said the claims had "no merit" and Nissan said it was "committed to compliance in all markets in which we operate".
What are your views on car owners being possibly mislead by carmakers' emissions tests? Get in touch.
Toyota unit to settle emissions scandal for $1.6bn
Trial of former VW boss begins over 'dieselgate' scandal
VW to pay out £193m in 'dieselgate' settlement
Sign up for our Future Earth newsletter to get exclusive insight on the latest climate and environment news from the BBC's Climate Editor Justin Rowlatt, delivered to your inbox every week. Outside the UK? Sign up to our international newsletter here.
Hostages reuniting with families as Trump greeted with cheers in Israeli parliament
Trump touts 'dawn of a new Middle East' in address to Israeli parliament
Who are the released hostages?
Your nose gets colder when you're stressed. These thermal images show the change
'He's giving us a lot of joy' – Rashford's revival at Barcelona
'I'm too busy!' How to make time for your friends
'In an instant, they were gone': Small town mourns after Tennessee explosives factory blast
How will the EU's new border system work?
Can Scotland rouse themselves for World Cup finale?
By-election set to test Labour's century-long dominance in historic Caerphilly
When do the clocks go back in the UK?
US Politics Unspun: Cut through the noise with North America correspondent Anthony Zurcher’s newsletter
An all-star cast enters the ultimate game of deceit
Stephen Fry shares the soundtrack to his extraordinary life
Some of music history’s most shocking stories revealed
The secretary who made millions from her typos
Two in court accused of killing jailed singer Watkins
Witkoff praises PM aide's 'tireless efforts' on Gaza
Tommy Robinson refused to give phone PIN to protect 'journalistic material'
Mortgage rates creep back up as lenders show caution
'He just kept growing': Life with a 13-stone Arctic dog
Who are the released hostages?
Trump says he may send Tomahawk missiles to Ukraine
First German state visit to UK for 27 years announced
What happens next in Gaza ceasefire plan after hostage release?
Carmakers go on trial over emissions cheat claims
Copyright © 2025 BBC. The BBC is not responsible for the content of external sites. Read about our approach to external linking.